Table of Contents
Machine guarding is a critical safety measurement broadly used in industrial areas. It shows its importance enormously when workers have to deal with hazardous machinery and equipment.
You may have heard about several types of machine guarding in the market and the industry. It is vital to understand their differences, functions, and applications, especially if you are a worker in some sectors or an employee in industrial regions.
That said, we aim to discuss the top five types of machine guarding today in this post. We will talk about each type in detail to find out how they are different. If you are an operator, safety manager, or engineer, this post will certainly assist you in picking the right machine guarding to prevent accidents and comply with safety regulations.
What is Machine Guarding and a Machine Guarding Mesh?
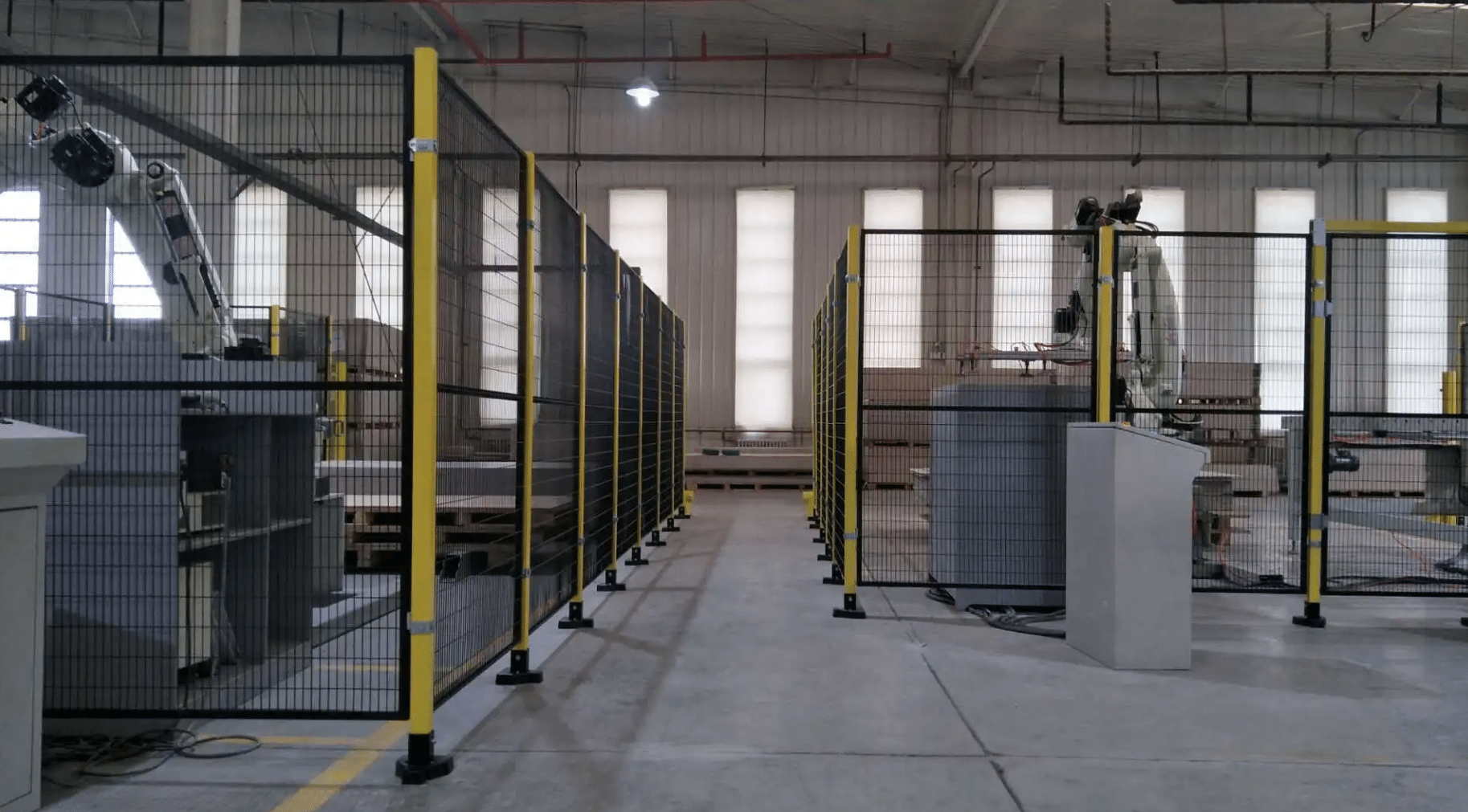

Machine guarding is a set of protective measures to shield workers against hazardous moving parts of a machine, including gears, belts, chains, and rotating mechanisms. It is widely employed in industrial machinery to guarantee the safe operation of machines for workers.
These measures are integral in preventing injuries like cuts, burns, or amputations. Guards can be physical barriers, devices, or protective enclosures that prevent workers from accessing unsafe areas. This way, only authorized personnel can work with the machinery during operation or maintenance.
A machine guarding mesh is a form of physical barrier used in machine guarding. It is made from materials such as steel or wire to shape a protective screen around the machine. It helps workers see the machine parts, and at the same time, prevents accidental contact with hazardous sections.
The strength and design of the mesh help it tolerate typical pressures in industrial areas. Plus, it provides airflow for proper ventilation, and lets workers monitor their machine operations in a safe way.
The Importance of Machine Guarding: Benefits and Drawbacks
Machine guarding is highly critical, particularly in industrial environments where the risk of injury is much higher. Below, we are going to discuss the reasons why machine guarding is important, and what we need to consider when using it.
Pros of Machine Guarding | Cons of Machine Guarding |
Injury Prevention | Initial Cost and Maintenance |
Compliance with Regulations | Potential for Reduced Efficiency |
Increased Productivity | Limited Access for Maintenance |
Protection of Equipment | Ergonomic Concerns |
Promotion of a Safety Culture | False Sense of Security |
Advantages of Machine Guarding
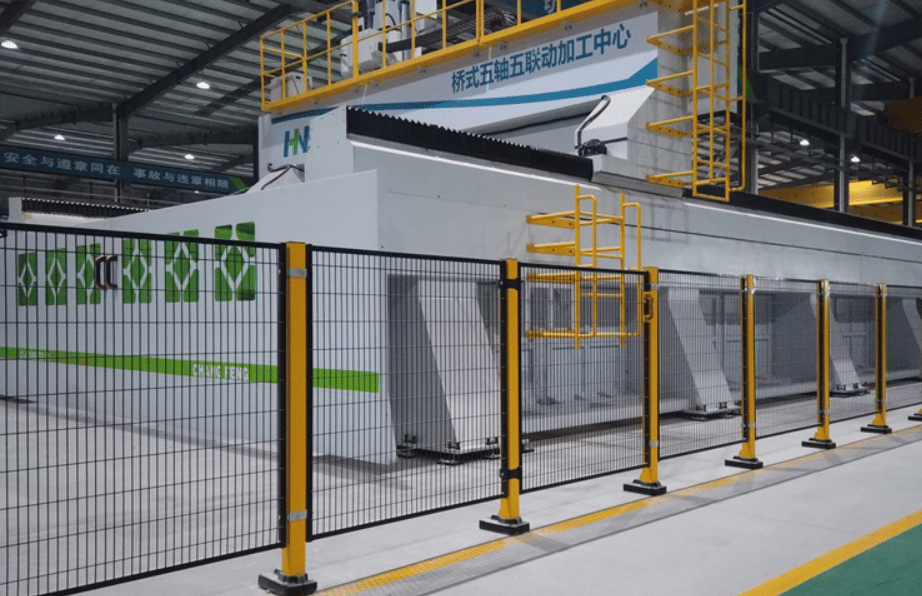

Machine guarding comes with diverse benefits that make it a necessary addition to any industrial setting. Here is why:
- Prevention of Injuries: First of all, machine guarding is employed to safeguard workers from injuries. Different pieces of equipment in factories and workshops have moving parts that can give birth to serious injuries such as cuts, fractures, or even amputations. Machine guarding, just like a barrier, prevents workers from touching these hazardous parts.
- Compliance with Regulations: In most regions, workplace authorities are coerced into using machine guarding for safety purposes. Regulatory officials like OSHA in the US specify strict standards for machine safety. Lack of compliance with these standards can result in massive fines, legal repercussions, and elevated scrutiny from regulatory agencies. It is critical to stick to these regulations through machine guarding to prevent potential risks.
- Enhancement of Productivity: When a working environment is safe, employees are more productive. This helps them feel safer, stay focused, and avoid accidents. Machine guarding prepares requirements for a safer workplace, resulting in heightened overall productivity and confidence among workers.
- Protection of Machinery: That is right; machine guarding is not just for workers; it can protect the machinery too. Machine guarding prevents unauthorized access and accidental damage. This way, they lengthen the lifespan of the equipment. That is because a well-maintained machine will face fewer breakdowns and demand less frequent repairs, which leads to notable cost-saving for the company.
- Promotion of a Safety Culture: Using machine guarding is in fact a smaller part of building the foundations of a safety culture inside a factory. It lets employees understand that their well-being is highly crucial for the company. This way, the loyalty of the employees is enhanced. Also, potential employees will be more willing to work for the company because of the deep focus on safety.
Disadvantages of Machine Guarding
Despite all the benefits of machine guarding, it also comes with some crucial considerations:
- Initial Cost and Maintenance: It can be costly to install machine guards, especially if the machinery is complex. That is mainly for purchasing the guards themselves and the labor needed for installation. Also, maintenance of these guards—which is highly crucial to guarantee their efficiency—can increase costs for users.
- Potential for Reduced Efficiency: In some specific cases, machine guarding can impact the efficiency of the machine. For instance, for the maintenance or setup of fixed guards, you have to remove them, which can be time-consuming. Adjustable and interlocked guards also need recurring repositioning or checks, which can disrupt workflow.
- Limited Access for Maintenance: Machine guards protect workers, but they may also restrict your access to the machine for maintenance and repairs. Therefore, it can become more challenging for technicians to maintain the machine routinely or detect issues in a flash, which may result in lengthened downtime.
- Ergonomic Concerns: Machine guards, if engineered improperly, can give birth to ergonomic issues for workers. Bulky or difficult-to-manipulate guards can cause strain or injury to workers who frequently work around them. That said, it is integral to consider proper ergonomics when designing these guards to handle this disadvantage.
- False Sense of Security: Relying solely on machine guards can generate a false sense of security for workers. They might unknowingly believe that machine guards can deliver complete protection, which can impact their watchfulness and make them neglect safety practices. To make sure workers will remain cautious, constant training is of high importance.
Which Parts of a Machine Must Be Guarded?
Machine guarding is integral for diverse sections of a machine. It is to make sure operators and other workers are all safe. Some crucial areas of a machine that must be guarded are as follows:
- Point of Operation: This point is where the machine does its job, such as cutting, shaping, boring, or forming materials. Guarding this point is integral because it is the point where the highest risk of injury lies, which might come from direct contact with the machine.
- Power Transmission Apparatus: These are the same components that transmit energy to the machine’s working parts. They include parts such as flywheels, pulleys, belts, chains, couplings, spindles, cams, and gears. They must be guarded with precision because of their moving nature and potential for entanglement.
- In-Running Nip Points: These points are also known as pinch points. They are areas where two parts move together, with one or both moving in a circular motion. Examples of these points are rollers, belt and pulley systems, and chain drives. Such points can trap/crush fingers or limbs, making guarding critical for them.
- Rotating Parts: As the name suggests, these are parts that rotate, including shafts, couplings, and pulleys. Risks of entanglement, drawing in clothing, hair, or limbs are innate in these parts. To prevent such hazards, accurate machine guarding is more than necessary.
- Reciprocating and Transverse Moving Parts: These parts move back and forth or side to side. Mechanical arms and cutting tools are among examples of these parts. Guarding these parts prevents workers from being struck/trapped as they work with the machine.
- Feed Mechanisms and Material Holders: These parts feed material for the machine. They may also hold materials in place as the machine works. Guarding these components is to make sure workers are shielded against accidental contact. Also, they ensure that the material is tight in place so the risk of mishandling or misalignment is minimized.
Types of Machine Guarding
Although machine guarding components and models are versatile, we decided to talk about five types that are more widespread.
Guarding Type | Flexibility | Protection | Maintenance | Cost |
Fixed Guards | Low | High | Low | Moderate |
Interlocked Guards | Moderate | Very High | Moderate | High |
Adjustable Guards | High | Moderate to High | High | Moderate |
Self-Adjusting Guards | High | High | Low to Moderate | Moderate to High |
Presence-Sensing Devives | Very High | Very High | Moderate to High | High |
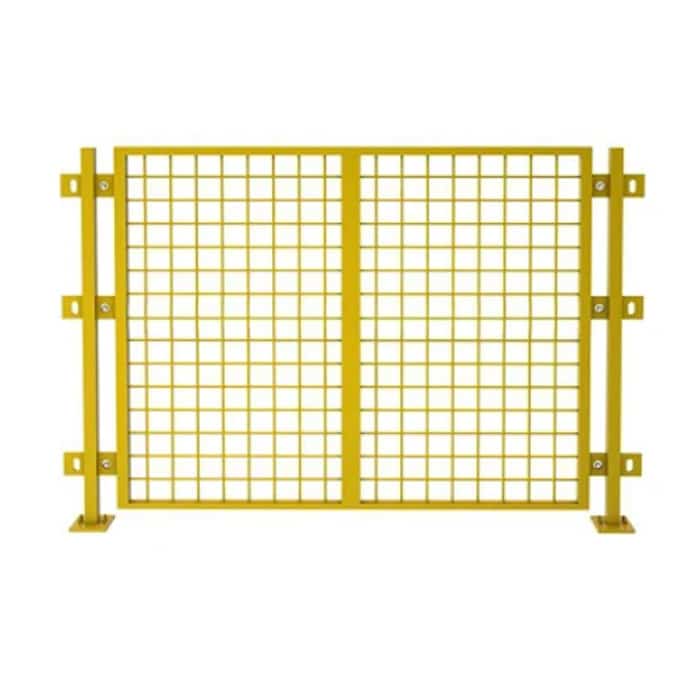
1. Fixed Guards
This type of machine guarding is known as a permanent barrier that is connected to a machine to deliver constant protection against moving elements. They are mostly crafted from metal or other durable materials. Their engineering allows them to entirely cover dangerous areas and prevent any contact with hazardous components.
As the name suggests, these guards are fixed in place. They do not need moving or adjusting during normal machine operation, which helps them deliver constant safety for workers.
Fixed guards are among the best options for machines that need less frequent access for maintenance and adjustment. Examples of these guards include guards around gears, chains, belts, and other power transmission components.
2. Interlocked Guards
These guards can automatically shut down the machine when the guard is opened/removed. This capability allows these guards to prevent access to hazardous elements of a machine when it is in operation.
Interlocked guards are armed with interlocking devices that connect to the machine’s control system. This is to make sure the machine will not operate unless the guard is secure in place.
These guards are wonderful options for machines that need routine access for maintenance, setup, or material changes. They are enormously secure because they can stop the machine instantaneously if the guard is tampered with or removed.
3. Adjustable Guards
These guards are highly flexible because they can be moved or repositioned. This feature enables them to house various sizes of material or changes in machine operation.
Operators can effortlessly modify adjustable guards to benefit from the required protection as the machine is in normal operation. These guards are specifically more beneficial in cases where the workpiece size changes repeatedly—including on drill presses, band saws, and certain woodworking equipment.
This is to say that adjustable guards can deliver adaptable safety. Still, they demand accurate positioning and securing to make sure they can provide their exact protection as the machine is operating.
4. Self-Adjusting Guards
Self-adjusting guards, as their name suggests, can automatically change their position according to the size and shape of the material being processed. They can move into the proper place as the material enters the machine, thereby guaranteeing the safety of the machine, even if the material is changed.
These guards are among the best guarding options for pieces of equipment that are supposed to handle diverse sizes and shapes of materials. Examples of this equipment include table saws and woodworking tools.
Since self-adjusting guards can automatically modify themselves based on each workpiece, they can eliminate the need for manual repositioning. This way, they can deliver steady protection and minimize the possibility of operator error.
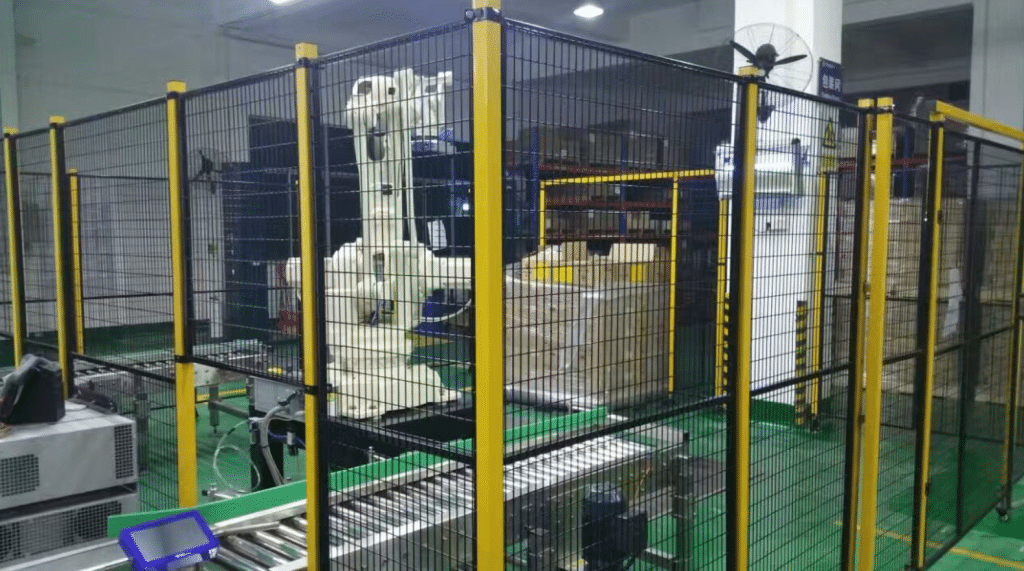
5. Presence-Sensing Devices
These guards detect the presence of a person or part of a person within a hazardous area. Upon this detection, they can stop the machine to prevent possible injury.
Presence-sensing devices include light curtains, pressure-sensitive mats, and laser scanners that together enable the guard to create an invisible field around hazardous parts of the machine. In the case that the field is breached, the machine will instantaneously shut down or be taken to a safe status.
These guards are perfect for areas where physical barriers are impractical but a maximum level of safety is mandatory, including in robotic work cells and automated production lines. They deliver dynamic protection because they can respond to potential intrusions in the blink of an eye.
Final Words
It is eventually very critical to choose the right type of machine guarding because it can guarantee the safety of workers and maintain the efficient operation of the machine. Each type of machine guarding we talked about today comes with its unique features in minimizing the risks of working with industrial machinery.
Choosing the correct type of machine guarding empowers companies and factories to shield their employees, and at the same time, boost the productivity of their operations and minimize their downtime.