Table of Contents
Temporary fences are known as fundamental mechanisms used to secure construction sites, manage crowds at events, or create boundaries for a short-term project. The design and materials used to craft these versatile barriers are constantly progressing so they can handle diverse demands.
These fences, if built well, can deliver both security and peace of mind, regardless of your intentions to use them: protecting a construction area, guiding event attendees, or managing agricultural spaces.
In our comprehensive post today, we aim to discuss different types of temporary fences, the correct steps to install one, their pros and cons, and their expected lifespan.
What is a Temporary Fence?
A temporary fence is a freestanding barrier that can support itself. It is designed for short-term usage and secures/delineates an area. These fences are manufactured from panels that interlock using their couplers, hence their more effortless installation and removal.
Temporary fences are crafted in diverse types and form factors, including:
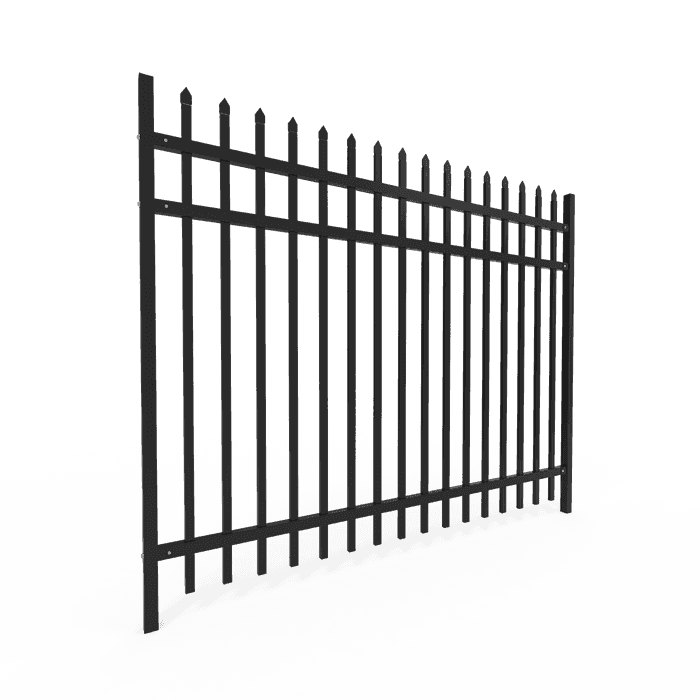
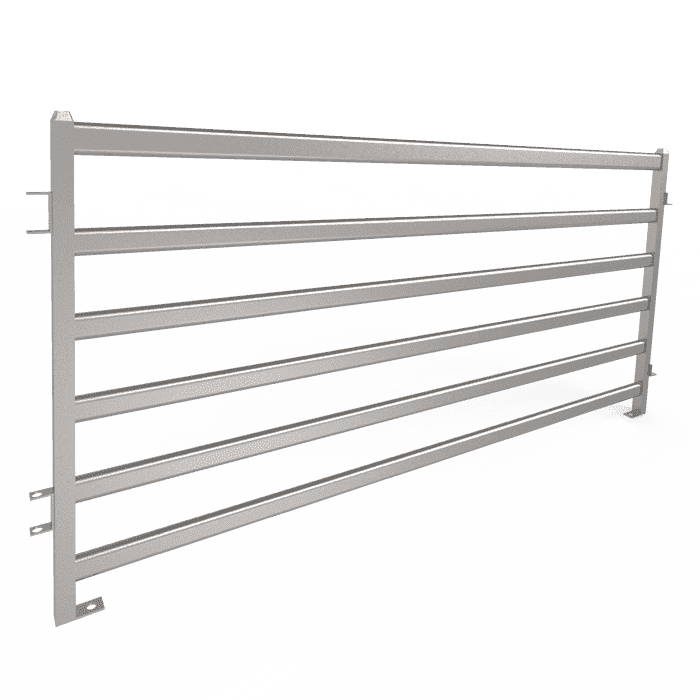
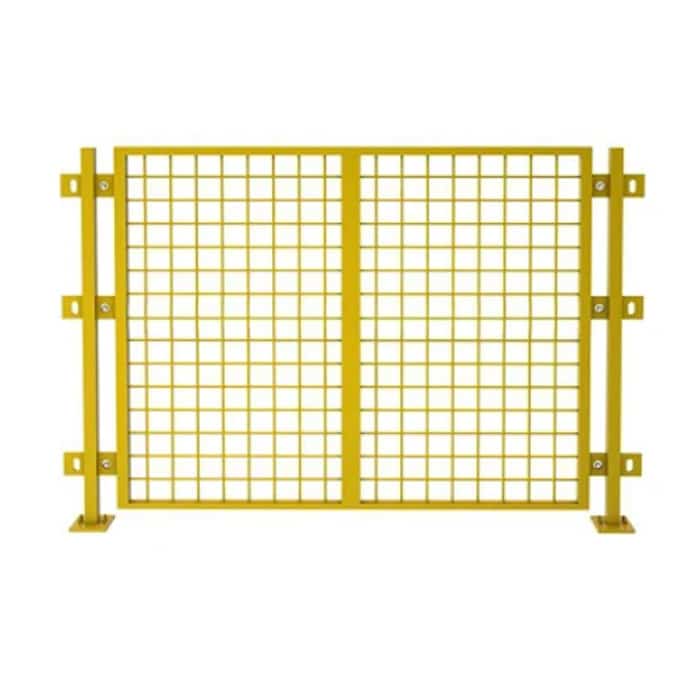
- Chain Link Panels: In this type, chain link fabric is connected to metal frames to deliver a mighty and transparent barrier for construction sites.
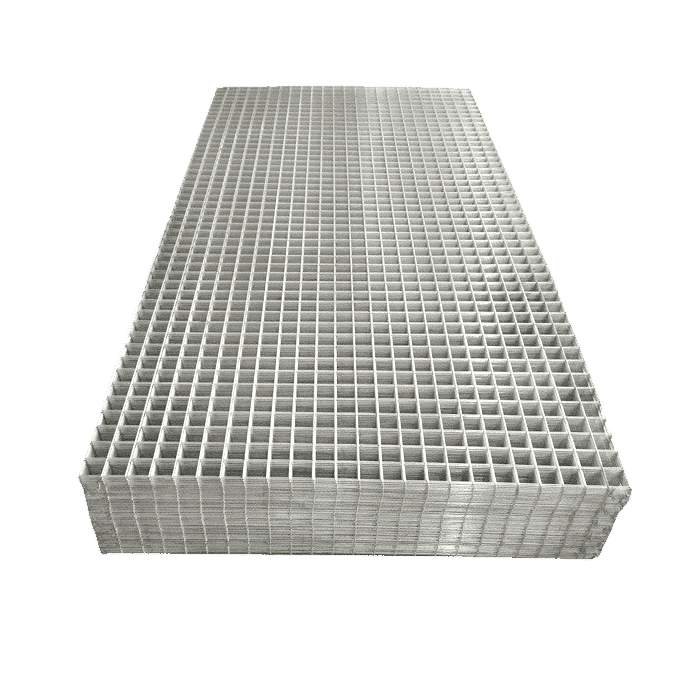
- Welded Wire Panels: This type is armed with a grid of welded wires so panels can deliver strengthened rigidity, hence a wonderful choice for both security and crowd control.
- Heras Fencing: This system is more popular in the UK and contains easy-to-install metal mesh panels that provide strong security for multiple uses.
- Crowd Control Barriers: This type is engineered to handle large crowds, like at events where guided traffic and unauthorized entrance are of critical importance.
Temporary fences are used in different applications, some of which are:
- Construction Sites: These fences deliver safety and security in construction sites as they prohibit disallowed entrances and shield the public from hazards.
- Public Events: Events such as concerts, festivals, and sports games are where temporary fences are employed to manage crowds, designate specific areas, and strengthen security standards.
- Emergency Situations: During emergencies, these fences can be used to quickly secure perimeters, control access, and protect susceptible regions.
- Agricultural Uses: Agricultural areas can benefit from these fences for purposes such as rotational grazing where livestock is routinely moved between pastures.
The Correct Steps to Building a Temporary Fence
Constructing a temporary fence is critical in securing construction sites, managing crowds at events, or specifying boundaries for short-term projects. The process contains several steps.
Step 1: Planning and Preparation
Planning and preparation are crucial primary steps to making sure the fence meets your certain requirements and standards.
Initially, you need to assess the area where you tend to install the fence. Measure the perimeter to find out how many panels you need. Make sure you consider the unique characteristics of the site: uneven terrain, slopes, or obstacles. This is to avoid complications later.
Then, it would be time to pick the right materials. Various types of fencing panels—including chain link and welded mesh—are available. Make sure your chosen material meets the standards for temporary fencing, which define the quality, strength, and safety of the materials.
Step 2: Gather Necessary Equipment
Once your plan is ready, collect all the equipment and tools needed for the installation. Accurate preparation will make the whole installation process highly effortless and straightforward.
A general list of your required equipment and tools can contain:
- Fencing Panels: Prepare enough panels to cover the entire perimeter of the area. In most cases, you will need chain links or mesh panels.
- Posts and Bases: Posts are used as vertical support for the fence, and bases as additional stabilizers—especially on hard surfaces. Both of them are critical to ensuring the fence will remain secure.
- Connecting Hardware: Clamps, couplers, or brackets are needed to connect the fencing panels to the posts. These connectors stabilize the structure strongly, especially in windy conditions.
- Tools: Common tools needed for the installation are a post hole digger to create holes, a hammer to secure posts and connectors, and a level to make sure the panels are aligned and direct.
Step 3: Mark and Prepare the Site
Before commencing the installation phase, you need to prepare and mark the site. To handle this, use stakes, strong, or spray paint to mark the area where the fence is to be installed. This is like a guide for digging post holes and placing the panels.
Then, dig post holes for the fence posts at uniform intervals—usually 2.5 meters apart. The depth of each hole should be roughly 600mm (24 inches) to make sure posts are supported appropriately.
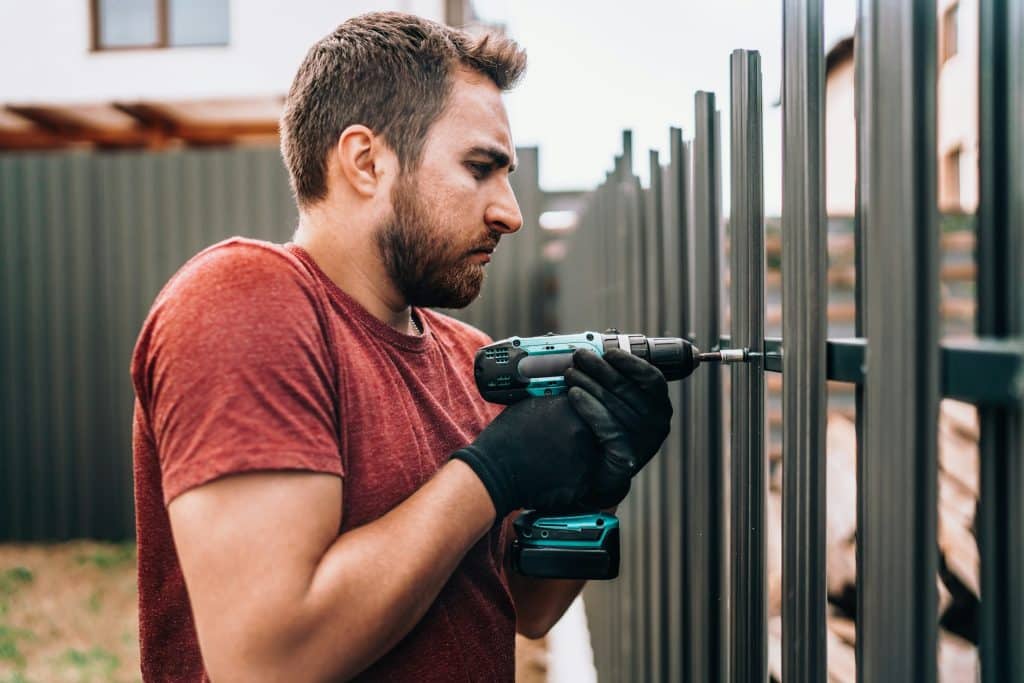
Step 4: Install Fence Posts
The next step is to install the fence posts. First, place a post in each hole such that it is aligned with the marked fence line. Use a level to confirm the post is vertical. That’s because any misalignment can weaken the stability of the fence.
Then, backfill the hole with soil/gravel. Compact it around the base to hold the post tight in place. Concrete can also be used when maximized stability is demanded.
Step 5: Attach Fencing Panels
Once the posts are secured, it will be time to initiate attaching the fencing panels.
- Position Panels: Start from one corner and place the first panel aligned with the first post. Make sure the panel is level before you secure it.
- Secure the Posts: Use proper clamps/couplers to attach the panel to the post. See if each panel is tightly connected to prevent sagging or movement.
- Continue Installation: Repeat the process for all panels. Check them occasionally to make sure alignment and spacing between posts and panels are appropriate.
Step 6: Stabilize the Fence
To make sure your fence will always remain secure, extra stabilization is of great importance. To handle this, you can install diagonal braces at crucial points along the fence—like corners and midway along each side. This is to prevent the fence from shifting or falling.
Then, walk around the fence perimeter to inspect it. See if there are any weak points, misalignments, or loose connections. Make necessary modifications to make the fence as stable as possible.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Temporary Fences
Temporary fences come with a set of notable advantages in addition to some considerations. Let’s review these benefits and drawbacks in detail.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Advantages of Temporary Fences
Temporary fences come with a bunch of benefits across their diverse applications. Such benefits make these fences an indispensable component of any construction site, event, and other short-term projects.
- Flexibility and Ease of Installation: Temporary fences come with an instantaneous and effortless setup with no need for a lot of groundwork or permanent foundations. This enables immediate deployment and adjustment if your requirements change.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Temporary fences are most of the time more cost-effective than installing permanent structures, especially if that’s for a short-term project. Not only is the initial investment lower but you can also rent panels to save money.
- Versatility: These fences are offered in diverse types, including chain link, welded wire, and panel fences. They can be customized to fit your desires. You are free to choose their height, material, and color based on your desire regarding the aesthetic and functional needs of the project.
- Basic Security and Safety: Temporary fences act as a physical barrier that deters unauthorized entrance and shields both the property and the inhabitants. They are employed to control crowds, handle pedestrian traffic, and delineate prohibited areas, hence maximizing safety.
- Compliance with Regulations: Temporary fencing is manufactured based on legal and safety standards set by authorities. This is to make sure construction sites and events surrounded by these fences can comply with all the required regulations. For example, in the UK, these fences must comply with specific regulations to guarantee their safety. These regulations include BS 1722-18:2011, which defines all the requirements for free-standing temporary steel mesh construction fence panels.
- Environmental Considerations: The majority of temporary fences are reusable and recyclable. This makes them fit all environmental sustainability goals. The modular essence of these fences lets them be used repeatedly, thereby lowering the need for new materials and minimizing waste.
Disadvantages of Temporary Fences
Although temporary fences deliver lots of benefits—especially due to their flexibility and cost-effectiveness for short-term needs—they come with certain disadvantages if you compare them with permanent fence options.
- Limited Durability and Stability: The effortless installation and removal of temporary fences considered during their manufacturing make them a bit less strong. This forces the manufacturer to craft these fences with lower sturdiness, so they may not be able to withstand harsh weather conditions or physical impacts. This can result in instability and damage.
- Lower Security Levels: Since these fences come with a lightweight and portable form factor, they are more susceptible to breaches. A normal person may find it uncomplicated to bypass or dismantle these fences. This can lead to security concerns, particularly in high-risk areas.
- Aesthetic Limitations: Although temporary fences are designed in a utilitarian form, they might lack the visual allure of permanent fences. For areas where appearance is of great importance—including residential areas or public events—this might be a major drawback.
- Regulatory Compliance Challenges: Temporary fences demand permits for installation. Also, they have to stick to specific codes. Handling such requirements might be intricate, and the lack of compliance might result in legal issues and fines.
- Harmful Materials for the Environment: Although the majority of temporary fences are reusable, some of their materials might not be environmentally friendly. This is more true about materials that are not properly disposed of or recycled after usage. Such materials can add to environmental waste and weaken sustainability efforts.
How Long Does a Temporary Fence Last?
The exact lifespan of a temporary fence hinges on several factors. These factors are listed below:
- Material Quality
- Chain Link Fences: These temporary fences are crafted from galvanized steel. They are enduring and able to withstand diverse harsh weather conditions.
- Vinyl Fences: These fences are lightweight and easy to install. Despite that, they might become brittle over time, especially when in very high temperatures.
- Wooden Fences: Although wood delivers a more naturalistic appearance, it is susceptible to rot, termites, and weather-related damage. This lowers the lifespan of wooden fences.
- Environmental Conditions: Harsh weather conditions—such as strong winds, heavy rain, or extreme temperatures—can expedite the process of wear and tear on temporary fences. For instance, lighter materials might not be able to withstand harsh weather conditions appropriately.
- Installation Quality: Accurate installation stabilizes the fence and lengthens its life cycle. Employing appropriate bases, secure connections, and correct tensioning are critical tasks that maximize the durability of these fences.
- Maintenance Practices: Routine inspections for damage, rust, or instability prepare you for in-time repairs, thereby extending the fence’s lifespan. Also, proper storage when the fence is not in use prevents potential wear and tear.
It should be noted that the lifespan of temporary fences can be somewhere between several months and a few years, depending on the aforementioned factors. For example, a chain link temporary fence that has been maintained properly can last longer than a vinyl or wooden fence that is exposed to analogous conditions.
There are some approaches to prolonging the lifespan of temporary fences. You can choose your materials based on your specific environmental conditions. Also, you must install the fence professionally if you want to extend its lifespan.
Routine maintenance and periodic checks help you prevent potential problems. Plus, you need to store your fence in a dry area to prevent damage.
Final Words
It is generally a straightforward but critical task to build a temporary fence because it eventually guarantees safety and security in diverse settings. That is why it is integral to understand the correct materials, installation steps, and maintenance practices so you can lengthen the lifespan and efficiency of your temporary fence.
Although these fences deliver heightened flexibility, affordability, and ease of installation, you need to consider their minor drawbacks such as some limitations in the case of durability and security. Considering your environmental conditions and sticking to proper regulatory standards allows you to make sure your temporary fence is highly dependable and compliant with industry standards.